
by MBF Admin | Jul 24, 2019 | 2D materials, Aerospace, AGM, Angstron Materials, Audio, Development, Graphene applications, Investment, OLEDs, Products, Research, Technical / Research
Paragraf, which recently raised $16 million USD to push forward graphene-based electronics technologies, and Queen Mary University of London have been awarded £500,000 (around $623,000 USD) by Innovate UK to explore using graphene to replace the rare metal Indium.The...

by MBF Admin | Jul 23, 2019 | 2D materials, Aerospace, AGM, Angstron Materials, Audio, Development, Energy storage, Graphene applications, Graphene coating, Graphene composites, Graphene EMI Shielding, Investment, Products, Research, Technical / Research
Sweden-based startup Graphmatech announced the launch of a new graphene-enhanced composite material. The new product, called Aros Create, is made of Nylon Aros Graphene pellets with a volume resistivity of less than 1 Ωcm while maintaining polymer lightweight,...
by MBF Admin | Jul 22, 2019 | 2D materials, Aerospace, AGM, Angstron Materials, Audio, Boron Nitride, Development, Graphene applications, Investment, Magnetism, Products, Research, Technical / Research, University of Manchester
Researchers from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) in Switzerland and the University of Manchester in the UK have found an efficient way to control infrared and terahertz waves using graphene. “There exist a class of the so-called Dirac materials, where the...
by MBF Admin | Jul 18, 2019 | 2D materials, Aerospace, AGM, Angstron Materials, Audio, Band gap, Boron Nitride, Conductors, Development, Graphene applications, Investment, Products, Research, Technical / Research
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have designed a graphene device that switches from a superconducting material to an insulator and back again to a superconductor — all with a flip of a switch....

by MBF Admin | Jul 14, 2019 | 2D materials, Aerospace, AGM, Angstron Materials, Audio, Development, Graphene applications, Graphene composites, Graphene Ink, Graphene Oxide, Graphene production, Graphene Sensors, Investment, Products, Research, Technical / Research, Transistors
Researchers at the U.S-based University of Rochester, along with colleagues at Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands, have designed a way to produce graphene materials using a novel technique: mixing oxidized graphite with bacteria. Their method is...
by MBF Admin | Jul 10, 2019 | 2D materials, Aerospace, AGM, Angstron Materials, Audio, Development, Graphene applications, Graphene composites, Investment, Medicine, Products, Research, Technical / Research
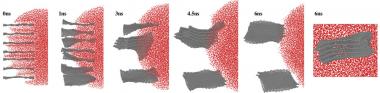
Researchers at the New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT) used the Comet supercomputer at the San Diego Supercomputer Center (SDSC), located at the University of California San Diego, to create detailed simulations of graphene-water interactions, to determine if...






